背景
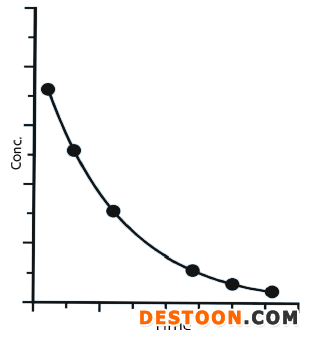
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">受试者服用溶液剂后,药物在体内没有释放过程,会被快速吸收,并分布及代谢和消除。所获得的血药浓度-时间曲线,如图1所示。溶液剂不涉及药物溶出过程,在体内的吸收系数、分布体积、消除系数均与原料药本身的药动学参数相关,药物在体内的浓度可用指数方程C= C0e-ktportant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">来描述。
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">当受试者服用固体制剂后,药物首先在胃肠道中溶解,形成溶液后再吸收,然后分布,代谢及消除。所获得的血药浓度—时间曲线,如图2所示。固体和液体制剂的药动学曲线不同,是由于服用固体制剂后,药物在体内会有缓慢释放过程,而液体制剂没有释放过程。
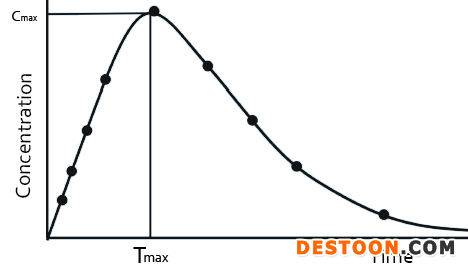
由溶液制剂的药动学曲线可知,药物形成溶液后,在体内的转运,仅与原料药自身的药动学参数有关。固体制剂的药动学曲线,则与药物在体内的溶解过程和药物的本身属性相关。而药物在体内的溶解过程,可以用药物的溶出曲线来表示,这也是体内外相关性模型建立的基础。
一般来说,药品的溶出不会改变药物的药代动力学,即药物的药动学参数,不会由于溶出的变化而变化。但不同的药品的溶出曲线,能影响药物在体内的溶解释放速度,从而影响血液浓度—时间曲线。由此可知,药代动力学为药物的基本属性,溶出则是药品剂型的属性。
IVIVR模型
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">体内外相关性模型,用IVIVR(in-vitro and in-vivo relationship)来表示,即将药品的体外特性(主要为溶出曲线)和体内特性(药动学)建立相关性。根据体外溶出数据,预测药物的在体内的药动学曲线,该方法为卷积法。相反,利用药物的吸收曲线,可预测药物在体内的溶出,该方法为反卷积法,如下图所示:
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">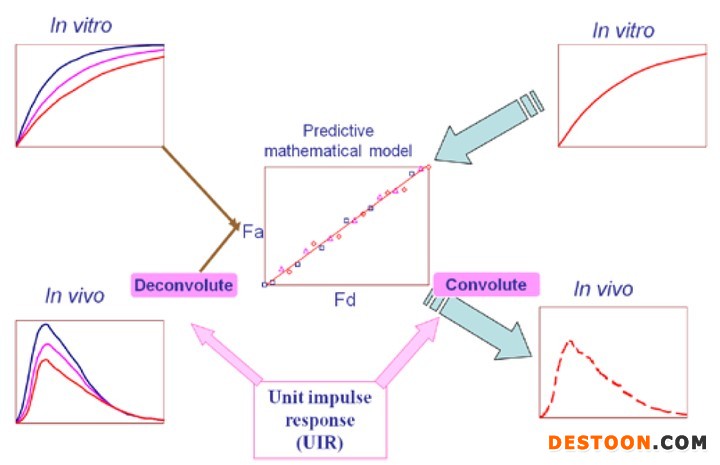
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">IVIVR模型类型较多,常用体内外模型[2]portant; letter-spacing: 0px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">的公式为:
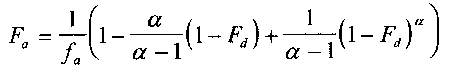
Fa:t时刻,药物吸收的总量,
fa:t 时刻,药物吸收的百分比,
α :一级渗透率常数(kpaap)与一级溶解率常数(kd)
Fd:t 时刻,药物溶解的百分数。
IVIVR模型在仿制药开发过程中,已有广泛的应用,文献报道[3,4],美托洛尔、吡罗昔康和雷尼替丁等项目,已成功利用该技术,进行处方工艺的开发。国内也应用IVIVR模型技术[5],建立不同剂型模型,实现了胶囊剂和分散片的生物等效性。
IVIVR应用案例
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">我司利用IVIVR模型,成功开发了盐酸曲美他嗪片。曲美他嗪片临床适用症为抗心绞痛药物,主要抑制游离脂肪酸代谢物,提高氧利用度,已缓解心肌缺血症状。体内外相关性模型中,输入的药物理化性质和药动学参数如下:
药物理化性质
a. 曲美他嗪BCS III类,极易溶于水
b. pKa 4.45和 9.14 ,log P 1.04
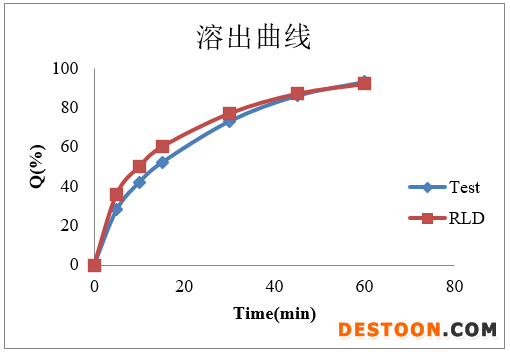
c. 溶出曲线:
药动学性质
a. 口服后,快速吸收,达峰时间少于两小时
b. 单次口服20毫克,达峰浓度约为55ng/ml
c. 连续给药在24至36小时达到稳态,体内稳定性好
d. 表观分布容积为4.8 L/ kg,具有良好的组织分布特性
e. 蛋白结合率低:其体外测量值为16%
f. 消除主要在尿液中,主要以原型药形态,平均消除半衰期为6小时
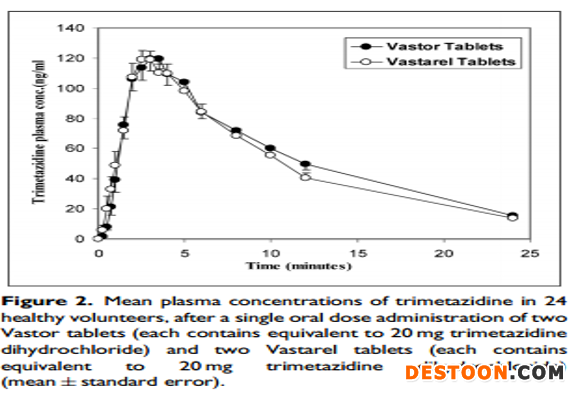
参考文献[6]“In vitro dissolution and in vivo bioequivalence evaluation of two brands of trimetazidine tables”,盐酸曲美他嗪片的药动学曲线如下:
 、
、
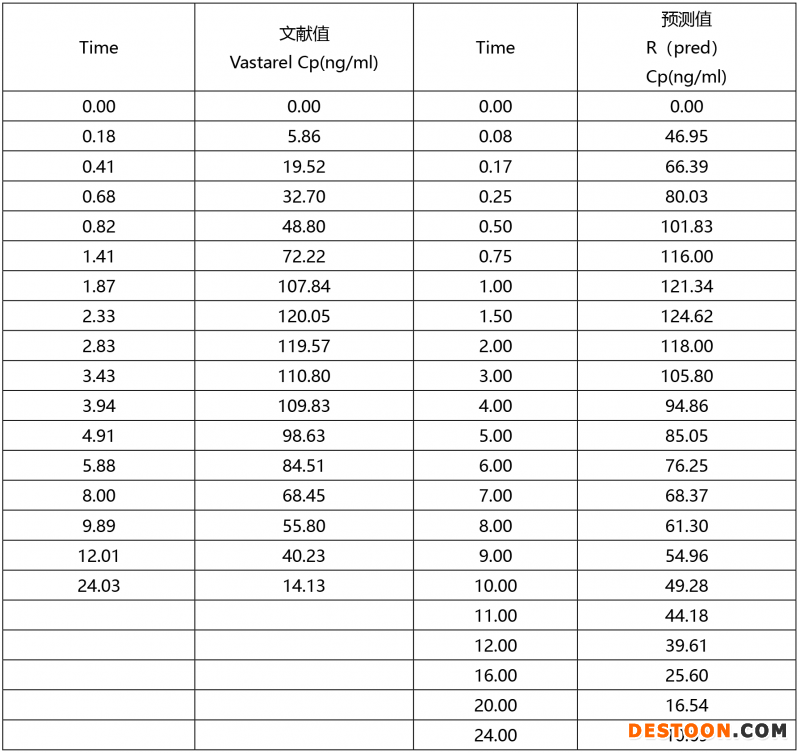
portant; letter-spacing: 0px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">尝试将曲美他嗪体外溶出行为和体内吸收建立相关性,利用卷积计算方法,预测药物在体内吸收。并将预测结果与文献数据进行对比,判断预测的准确性。文献值与预测值对比:
portant; letter-spacing: 0px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">文献值和预测值的PK曲线:
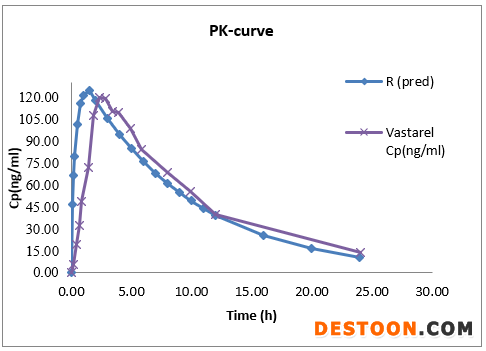
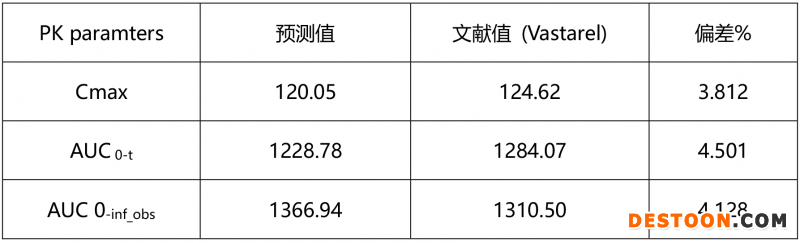
上述数据表明,曲美他嗪体内外模型相关性较好,PK参数预测值与文献报道值预测误差低于5%。该模型可成功预测体内吸收。
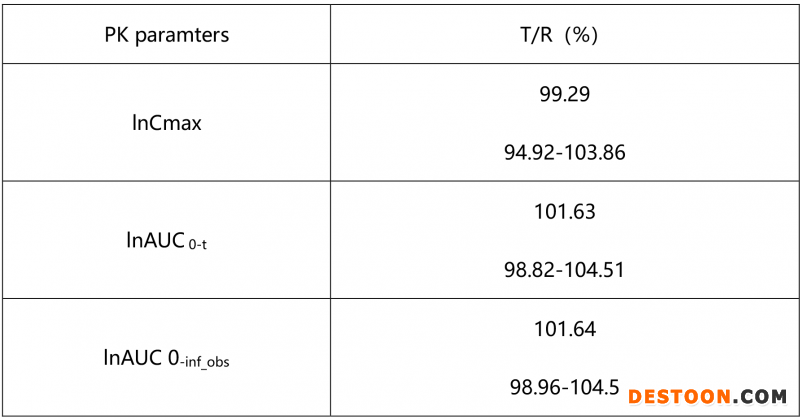
我方在完成注册三批样品后,溶出曲线如图4所示,根据已建立好模型,对其体内进行预测,所获得数据较好。因此本品种未进行预BE试验研究,直接进行BE试验,空腹条件下,所获得结果如下表:
portant; letter-spacing: 0px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">从溶出曲线可知,盐酸曲美他嗪片自制品和参比制剂的溶出能够拟合,体内外相关性模型,较容易建立。但在仿制药开发过程中,我们通常会遇到自制品很难与参比制剂在各个介质中拟合;不同批次参比的溶出差异较大;由于原料药溶解性较好,不能找到具有区分力介质等等问题,后续也会针对上述情况,进行系列模型建立的分享。
IVIVR未来应用
IVIVR模型是将溶出曲线和体内药动学行为进行结合,如何确保模型的稳健性,则需要对制剂工艺具有深入的了解及研究,同时也要考虑药动学参数的影响,如药物的渗透性、体内的降解等。
IVIVR模型应用逐渐广泛,不仅可以指导仿制制剂开发,对于新药开发也具有指导意义,如新药研发过程中,人体初始剂量的选择、药物之间的相互作用等。
参考文献:
-
USP 23-NF 18; United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., Rockville, MD, 1994.
-
J.E. Polli, J.R. Crison, and G.L. Amidon, Novel approach to the analysis of in vitro-in vivo relationships, J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 753-760 (1996).
-
E. Galia, E. Nicolaides, D. Horter, R. Lobenberg, C. Reppas, and Dressman JB, evaluation of various dissolution media for predicting in vivo performance of class I and II drugs. Pharm Res. 15, 698-705 (1998).
-
J.E. Polli, G.S. Rekhi, L.L. Augsburger, and V.P. Shah, Methods to compare dissolution profiles and a rationale for wide dissolution specifications for metoprolol tartrate tablets, J. Pharm. Sci. 86, 690-700 (1997).
-
Candy wang, IVIVR在剂型设计中应用,新领先药讯.
-
Sally A. Helmy and Noha O. Mansour. In vitro dissolution and in vivo bioequivalence evaluation of two brands of trimetazidine tables, Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development. 3(2)139-143.
-END-
关于我们:
北京新领先建立有体内外桥接平台,致力于将体内行为与体外行为进行桥接,利用软件建立体内外相关模型,明确药学开发目标,预测BE成功率,缩短药物研发时间,节约产品开发成本,为客户每个项目顺利申报提供保障。
本平台也针对客户在BE试验设计和结果所遇到的问题,提供技术支持,并提供合理、科学的建议。后续着重模型开发,扩大模型应用,为新药研发提供科学依据。本平台拥有或计划拥有全球应用最广泛的模型模拟软件和药动学分析软件,包括DDDPlus、ADMET predictor、Gastroplus、DAS、PASS、Phoenix WinNonlin等多种软件。
已经成功对近200个口服固体制剂项目开展了包括药学目标设定、预BE及正式BE的预测和结果分析解读等研究工作,其中进入到BE阶段的近百个项目,一次性通过率超过80%。此外,平台还对外承接了几十个BE预测及结果分析解读的项目,均精准剖析了客户于BE试验过程中存在的问题,并提供了合理完善的指导方案。
体内外桥接平台负责人为hemanth Joshi先生,曾担任世界排名前十通用名药企Dr.Reddy‘s Laboratories、Sun Pharmaceuticals等公司的高级科学家,拥有近20年的药物制剂研发及临床评价经验;曾参与几十个FDA、EMA注册ANDA、505b(2)的研发工作,其丰富的工作经历和卓越的工作能力,带领新领先医药研发水平更上一层楼。
portant; letter-spacing: 1px; background-color: rgb(255,255,255); text-indent: 0px; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; -webkit-text-stroke-width: 0px">体内外桥接平台服务范围
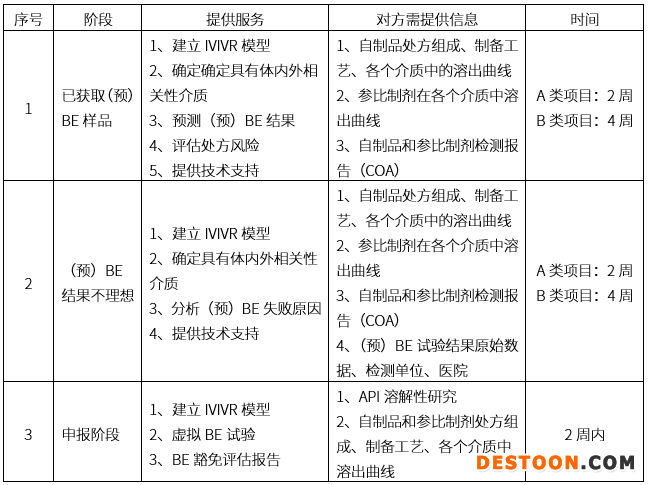
备注:
A类项目:普通速释制剂
B类项目:特殊缓控释制剂
时间计算为获得全部数据后,报告提供的时间


